
According to the statistical data one out of every 130 people has epilepsy, which is more than 50 millions of people all over the world. This is a chronic neurological disorder, commonly characterized by seizures, due to excessive hyper-synchronization of neurons in the brain. Epilepsy is usually diagnosed in young children or elderly people (over 65 years of age), but it can occur at any age.
How severe the seizures are depends on the type of epilepsy and the patient. Certain types of epilepsy do not look like seizures but more like trance and patients seem not to be present for a moment or several minutes. However, there are types of epilepsy in which the patient loses his/her consciousness and starts to shake uncontrollably, biting the tongue and foaming the mouth.
Epilepsy is a chronic condition and most patients can manage this problem with some of anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs). However, statistics reveal that about 30% of epileptic patients do not respond well to these drugs or any other treatment.
Epilepsy Types
Doctors differentiate three types of epilepsy, depending on the causes which provoke the condition. Symptomatic epilepsy is caused by some brain damage (head injuries or trauma) or disruption to the brain, while idiopathic epilepsy has no apparent cause. Another form of epilepsy is cryptogenic epilepsy. Patients suffering from this type of epilepsy experience learning problems and some other symptoms. Doctors cannot find any damage to the brain in these patients, but his/her symptoms suggest there must be some kind of brain abnormalities.
Known Causes and Triggers of Epilepsy
Symptomatic epilepsy may be a result of some birth defects. The baby deprived from oxygen at birth, because of the compression during birth or twisting of the umbilical cord may experience epileptic seizures. Meningitis and other infections that can damage the brain, as well as abuse of alcohol and drugs in pregnancy may lead to development of symptomatic epilepsy. Other possible causes of this condition are cerebral palsy, head injuries, stroke or brain tumors.
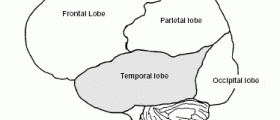
Doctors cannot find the exact cause of cryptogenic epilepsy but there are certain signs pointing to some brain damage. These patients suffer from developmental and learning problems and their EEG (electroencephalogram, reading of the electrical activity of the brain) is often unusual, suggesting brain problems.
Idiopathic epilepsy has no apparent cause, but doctors believe this condition is provoked by some genetic changes and problems. Some ongoing researches are looking into genes that might be responsible for these epileptic seizures, but no such gene has been identified so far.
Many patients found that there are certain things which can trigger epileptic seizure. These involve intake of alcohol or some illegal drugs, high temperature, stress or lack of sleep. Female patients may have seizures associated with their menstruation and hormonal changes during that period. Flashing light is also identified as epilepsy trigger and may cause photosensitive epilepsy.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...