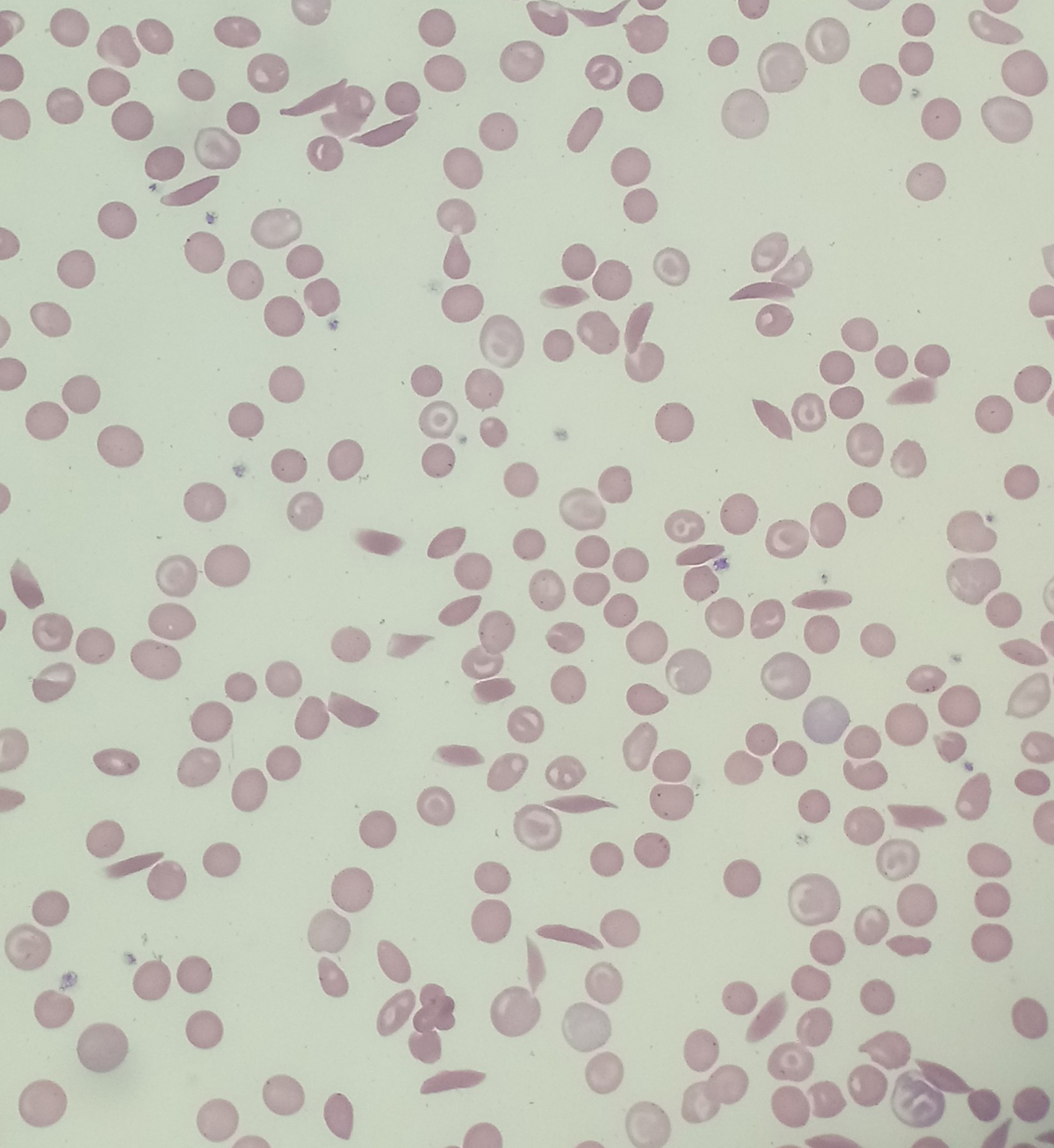
Fanconi anemia is a serious genetic problem which in most cases has to be treated. Patients may have different problems because of this disease. The treatment depends on the condition of the bone marrow and its ability to produce red and white blood cells and platelets. Commonly used therapies for Fanconi anemia (FA) are bone marrow transplant, gene replacement therapy and treatments with hormones and hematopoietic growth factors.
Besides these treatments, patients are frequently checked for cancers and educated to minimize the risk regarding agents known to damage DNA even further.Fanconi Anemia: Transplantation of the Bone Marrow
Bone marrow transplant is a standard procedure for FA patients who experience bone marrow failure (aplastic anemia). Allogeneic transplantation is the process of using donor’s blood cells and it is very successful if the donor is a sibling, usually patient’s brother or a sister. There are certain risks associated with this treatment, such as graft rejection or graft versus host disease (GVHD). Doctors may, therefore, use some medications and therapies, to decrease the risks of these unwanted reactions. However, doses of these therapies must be modified for FA patients because some of them are known to have toxic potential.
Gene Replacement and Other Therapies for Fanconi Anemia
Another available treatment for FA is gene replacement therapy. Doctors collect patient’s own blood cells with A or C complementation group defect and correct mutated FA gene. Corrected copy is then transferred to these cells and then transplanted into the patients. The risk of graft rejection or immune reactions is lower because these are patient’s own cells and not someone else’s. These corrected and transplanted cells live longer than non-corrected cells and this is why doctors believe the treatment will support the bone marrow and decrease the risk of FA relapse.
Hormone or otherwise known as androgen treatment is option for patients who do not have appropriate donor for bone marrow transplant. In some 50% of treated patients androgen therapy successfully improves the blood counts, but the treatment lasts for 12 and even more moths in order to give good results and improve the count of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. There are some side effects of such treatment like acne, oily skin, voice changes, growth or loss of hair, hot flashes, enlargement of breasts, clitoris or penis, retention of water, high blood pressure or even cholestasis or elevated liver enzymes, as well as other problems.
Growth factor may also be used in some FA treatment in order to improve the counts of red blood cells and platelets.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...